What is Edge Computing?
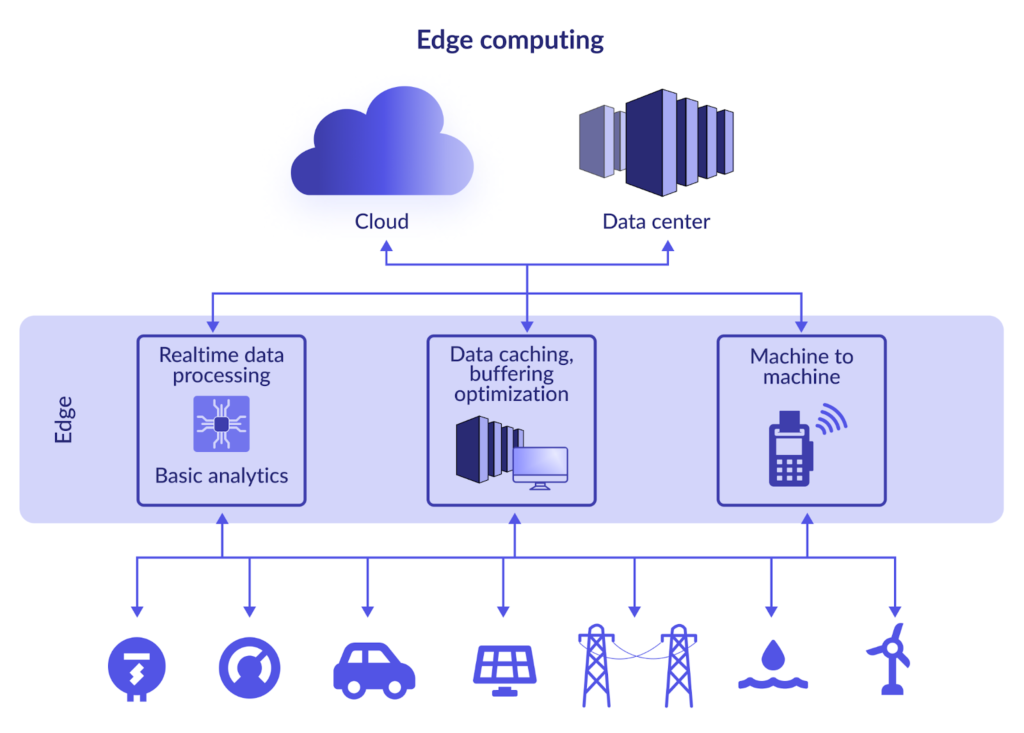
Edge computing is a transformative technology that processes data at the periphery of the network, near the source of the data. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which centralizes data processing in remote data centers, edge computing brings computation and storage closer to the devices generating the data. This paradigm shift aims to reduce latency, enhance speed, and improve overall efficiency in data management.
Key Benefits of Edge Computing
- Reduced Latency: By processing data locally, edge computing significantly reduces the time it takes for data to travel between devices and central servers. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
- Improved Bandwidth Efficiency: Edge computing minimizes the amount of data sent to central servers, reducing bandwidth usage and costs. This is particularly beneficial for IoT (Internet of Things) devices that generate massive amounts of data.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: Processing data at the edge can enhance security by limiting the exposure of sensitive information to the broader network. Local data processing can also help organizations comply with data sovereignty regulations.
- Reliability: Edge computing can improve the reliability of applications by decentralizing processing tasks. If one node fails, others can continue to operate, ensuring continuous service.
Applications of Edge Computing
- Internet of Things (IoT): Edge computing is a cornerstone of IoT deployments, enabling smart devices to process data locally and act on it in real time. This is essential for smart homes, cities, and industrial IoT applications.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on edge computing to process data from sensors and cameras instantly, allowing for rapid decision-making and enhancing safety.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, edge computing enables real-time monitoring and analysis of patient data, facilitating timely interventions and improving patient outcomes.
- Retail: Retailers use edge computing for inventory management, personalized customer experiences, and efficient checkout processes through technologies like smart shelves and automated checkouts.
Challenges of Edge Computing
- Infrastructure Costs: Implementing edge computing requires significant investment in infrastructure, including edge devices and local data centers.
- Data Management: Managing data across a distributed network can be complex, requiring robust solutions for data synchronization and consistency.
- Security Concerns: While edge computing can enhance security, it also introduces new vulnerabilities that need to be addressed, such as securing edge devices and ensuring secure data transmission.
Future of Edge Computing
The future of edge computing is promising, with advancements in AI and machine learning further driving its adoption. As more devices become connected and generate data, the need for efficient, real-time processing will continue to grow. Innovations in edge computing will enable smarter cities, more efficient industries, and enhanced user experiences across various sectors.
Conclusion
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way we process and manage data. By bringing computation closer to the source, it reduces latency, enhances efficiency, and opens up new possibilities for real-time applications. As the technology continues to evolve, its impact on industries and everyday life will only expand, making edge computing a critical component of the digital future.